It's suddenly all over the news. In hindsight, it was a matter of "not if, but when".
Sophos just warned against a new hybrid worm that combines the ETERNALBLUE exploit and cryptomining.
ETERNALBLUE is the infamous escaped NSA code that was used in the WannaCry worm, so the combination of this method of breaking in, followed by a cryptomining payload, has been dubbed WannaMine.
WannaMine attacks aren’t new, but the Sophos Support team has recently had a surge in the number of enquiries from people asking for advice about the issue. Sophos posted a 13 minute video interview.
Here are the quick Questions and Answers, based on the video.
Q. Is WannaMine like WannaCry? Is it ransomware that scrambles my disk?
A. The name “WannaMine” is a coined term (pun intended) that refers to a malware family that uses the network spreading capabilities of WannaCry to deliver cryptomining malware rather than ransomware.
Q. What is cryptomining malware? Is it as dangerous as ransomware?
A. Cryptomining is when crooks secretly get your computer to do the calculations needed to generate cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, Monero or Ethereum; the crooks keep any cryptocoin proceeds for themselves.
To make money with cryptomining, you need a lot of electricity to deliver a lot processing power on a lot of computers.
By illegally installing cryptominers inside your network, the crooks therefore steal your resources to do their work.
Q. Can cryptomining damage my computer?
A. We’ve seen stories of mobile phone batteries bulging due to overheating when the device was deliberately forced to do mining calculations for hours on end.
However, WannaMine doesn’t run on mobile phones – it attacks Windows computers.
Nevertheless, even if no permanent damage is done, you’ll probably find your laptop batteries draining much faster than usual, your fans running flat out, and your laptop being noticeably hotter than usual.
Also, if malware like WannaMine can penetrate your network, you are at serious risk of other malware at the same time, including ransomware.
We frequently see evidence of cryptomining left behind on computers that were zapped by ransomware, so don’t ignore WannaMine infections if they show up – where one crooks goes, others will surely follow.
Q. If I don’t own any cryptocoins and I’m not part of the cryptocurrency scene, am I still at risk?
A. Yes.
WannaMine malware attacks aren’t trying to locate your digital cryptocurrency stash and steal it.
They want free use of your computer for cryptomining calculations of their own, whether you’re interested in cryptocurrency or not.
Q. Can security software prevent WannaMine attacks?
A. Yes.
Exploit prevention software (e.g. Sophos Intercept X) can block the ETERNALBLUE attack to prevent malware like this from entering your network in the first place.
Anti-virus and host intrusion prevention software (e.g. Sophos Endpoint Protection) can stop the malicious processes that allow the WannaMine attack to proceed, even if the exploit triggers at te start.
Network security software (e.g. Sophos XG Firewall) can block the network activity required for malware like WannaMine to work.
Q. What else can I do?
A. Patch promptly, and pick proper passwords.
WannaMine malware typically includes the same ETERNALBLUE exploit that was abused by WannaCry and allowed it to spread. This exploit was patched last year in Microsoft update MS17-010, so a properly patched network wouldn’t be open to the exploit in the first place.
If the ETERNALBLUE hole is already closed, WannaMine can try to spread using password cracking tools to find weak passwords on your network.
Sophos said: It only takes one user with poor password hygiene to put your whole network at risk.
Here are three things you can do about this right now
-
Re-test your whole network for Patch MS17-010 and make 100% sure that all machines are indeed updated
-
Step your users through new-school security awareness training, and have them do the new Strong Passwords Module.
-
Download the free Weak Password Test tool, and immediately scan AD for passwords that need to be beefed up.
How weak are your user’s passwords? Are they... P@ssw0rd?
KnowBe4’s complimentary Weak Password Test (WPT) checks your Active Directory for several different types of weak password related threats.
WPT gives you a quick look at the effectiveness of your password policies and any fails so that you can take action. WPT tests against 10 types of weak password related threats for example; Weak, Duplicate, Empty, Never Expires, plus 6 more.
Here's how Weak Password Test works:
-
Reports on the accounts that are affected
-
Tests against 10 types of weak password related threats
-
Does not show/report on the actual passwords of accounts
-
Just download the install and run it
-
Results in a few minutes!
This will take you 5 minutes and may give you some insights you never expected!
Download Now:
https://info.knowbe4.com/weak-password-test
Warm regards,
Stu Sjouwerman
Founder and CEO, KnowBe4, Inc.








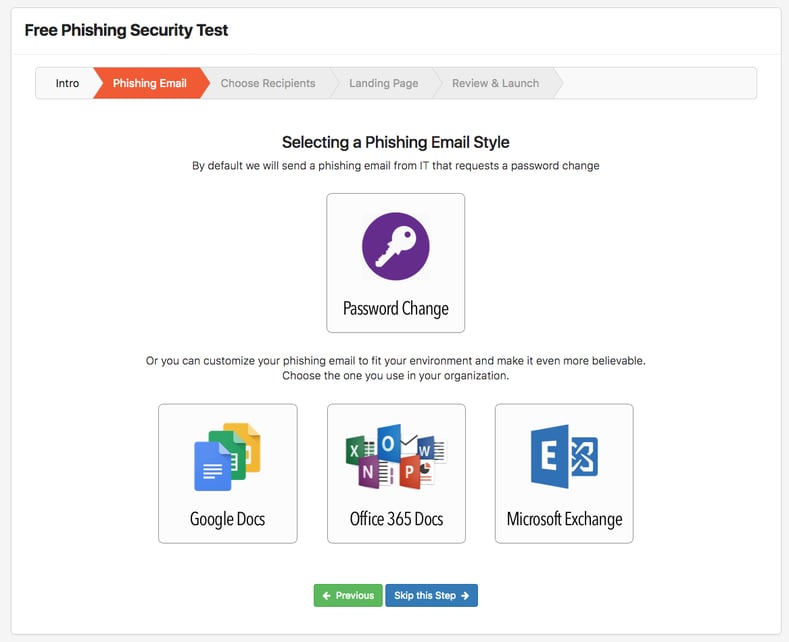

 with our free Phishing Security Test (PST). If you don't do it yourself, the bad guys will.
with our free Phishing Security Test (PST). If you don't do it yourself, the bad guys will.